Indications
Barhemsys is a selective dopamine-2 (D2) and dopamine-3 (D3) receptor antagonist indicated in adults for:
- prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV), either alone or in combination with an antiemetic of a different class
- treatment of PONV in patients who have received antiemetic prophylaxis with an agent of a different class or have not received prophylaxis
Important Safety Information
Contraindication
Barhemsys is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to amisulpride.
QT Prolongation
Barhemsys causes dose- and concentration-dependent prolongation of the QT interval. The recommended dosage is 5 mg or 10 mg as a single intravenous (IV) dose infused over 1 to 2 minutes.
Avoid Barhemsys in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients taking droperidol.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring is recommended in patients with pre-existing arrhythmias/cardiac conduction disorders, electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia), congestive heart failure, and in patients taking other medicinal products (e.g., ondansetron) or with other medical conditions known to prolong the QT interval.
Adverse Reactions
Common adverse reactions reported in ≥ 2% of adult patients who received Barhemsys 5 mg (N=748) and at a higher rate than placebo (N=741) in clinical trials for the prevention of PONV were: chills (4% vs. 3%), hypokalemia (4% vs. 2%), procedural hypotension (3% vs. 2%), and abdominal distention (2% vs. 1%).
Serum prolactin concentrations were measured in one prophylaxis study where 5% (9/176) of Barhemsys-treated patients had increased blood prolactin reported as an adverse reaction compared with 1% (1/166) of placebo-treated patients.
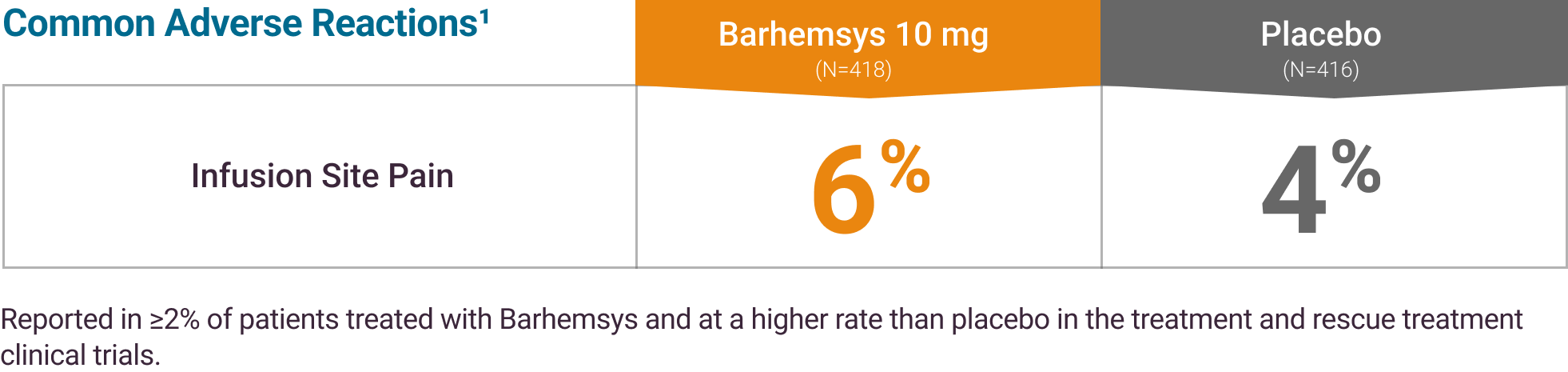
The most common adverse reaction, reported in ≥ 2% of adult patients who received Barhemsys 10 mg (N=418) and at a higher rate than placebo (N=416), in clinical trials for the treatment of PONV was infusion site pain (6% vs. 4%).
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Available data with amisulpride use in pregnant women are insufficient to establish a drug associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
Lactation
Amisulpride is present in human milk. There are no reports of adverse effects on the breastfed child and no information on the effects of amisulpride on milk production.
Barhemsys may result in an increase in serum prolactin levels, which may lead to a reversible increase in maternal milk production. In a clinical trial, serum prolactin concentrations in females (n=112) increased from a mean of 10 ng/mL at baseline to 32 ng/mL after Barhemsys treatment and from 10 ng/mL to 19 ng/mL in males (n=61). No clinical consequences due to elevated prolactin levels were reported.
To minimize exposure to a breastfed infant, lactating women may consider interrupting breastfeeding and pumping and discarding breast milk for 48 hours after receiving a dose of Barhemsys.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Drug Interactions
- Barhemsys causes dose- and concentration-dependent QT prolongation. To avoid potential additive effects, avoid use of Barhemsys in patients taking droperidol.
- ECG monitoring is recommended in patients taking other drugs known to prolong the QT interval (e.g., ondansetron).
- Reciprocal antagonism of effects occurs between dopamine agonists (e.g., levodopa) and Barhemsys. Avoid using levodopa with Barhemsys.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Acacia Pharma at 1-877-357-9237 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Please click to access full Prescribing Information.
BAR HCP ISI 09/2022